Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose), a vital source of energy for your cells. When left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to serious health complications. Understanding its types, symptoms, and management strategies is essential for living a healthy life.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes occurs when your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or cannot use the insulin it produces effectively. Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that helps glucose enter cells to be used for energy. Without proper insulin function, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to high blood sugar levels.
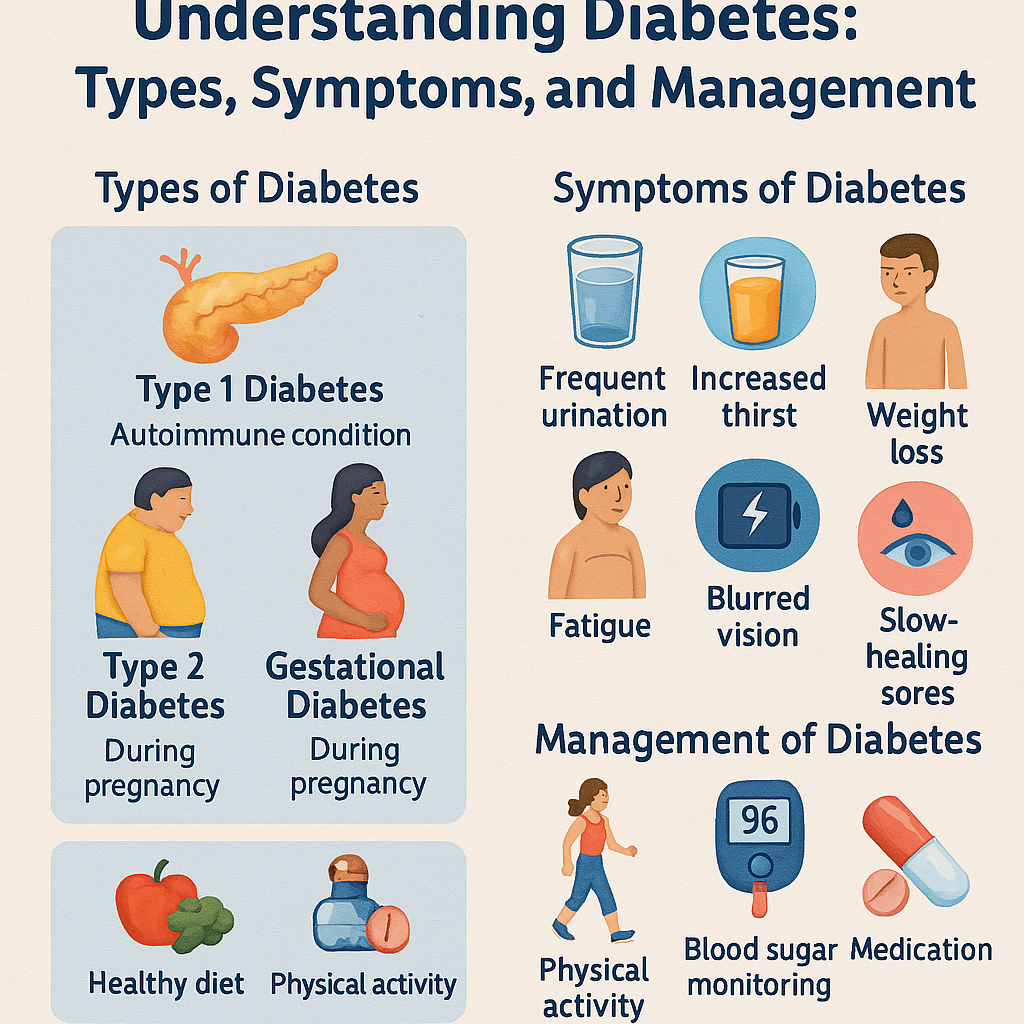
Types of Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Commonly diagnosed in children and young adults.
Requires daily insulin injections or use of an insulin pump.
- Type 2 Diabetes
More common and usually develops in adults.
The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough.
Often linked to lifestyle factors like obesity and inactivity.
Can be managed with diet, exercise, and medication.
- Gestational Diabetes
Occurs during pregnancy and usually disappears after childbirth.
Increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life for both mother and child.
- Prediabetes
A condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes.
Can often be reversed with lifestyle changes.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
Frequent urination
Excessive thirst
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue
Blurred vision
Slow-healing wounds
Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
Many people with type 2 diabetes may not show symptoms initially, which is why regular check-ups are important.
How to Manage Diabetes
- Healthy Diet
Focus on whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Limit sugar and refined carbs.
Monitor carbohydrate intake to control blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise
Improves insulin sensitivity.
Helps maintain a healthy weight.
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar
Track levels regularly to manage fluctuations.
Work with a healthcare provider to set target ranges.
- Medication or Insulin Therapy
May be required for type 1 diabetes or advanced type 2 diabetes.
Follow prescriptions and medical advice closely.
- Stress Management
Stress can affect blood sugar levels.
Use techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or engaging in hobbies to stay calm.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Maintain a healthy weight
Eat a balanced diet
Stay active
Get regular screenings, especially if you have risk factors like a family history or obesity
Conclusion
Diabetes is a manageable condition with the right lifestyle choices, medical care, and awareness. Understanding the types, recognizing the symptoms, and taking action early can prevent complications and ensure a better quality of life.
Take a Break and Reduce Stress with Flutter Bees
Living with or managing diabetes can be stressful, so why not take a fun break with Flutter Bees? This relaxing clicker and bee hive defense game is perfect for quick mental relief. Tap your way to rewards, complete engaging tasks, and watch your points grow. It’s a stress-free way to refresh your mind and recharge. Try it now:
Flutter Bees






Leave a Reply